Structural design of continuous zoom lens
- Share
- Issue Time
- Oct 31,2024
Summary
The continuous zoom lens works on the principle that the focal length of its optical system can be changed continuously within a certain range, and the image plane position remains unchanged during focal length adjustment. When it is not possible to change the focal power of the optical system directly, changes in focal length can only be achieved by adjusting the distance between each lens group, which is the fundamental principle of the zoom optical system.
Principle of zoom system
The continuous zoom lens works on the principle that the focal length of its optical system can be changed continuously within a certain range, and the image plane position remains unchanged during focal length adjustment. When it is not possible to change the focal power of the optical system directly, changes in focal length can only be achieved by adjusting the distance between each lens group, which is the fundamental principle of the zoom optical system.
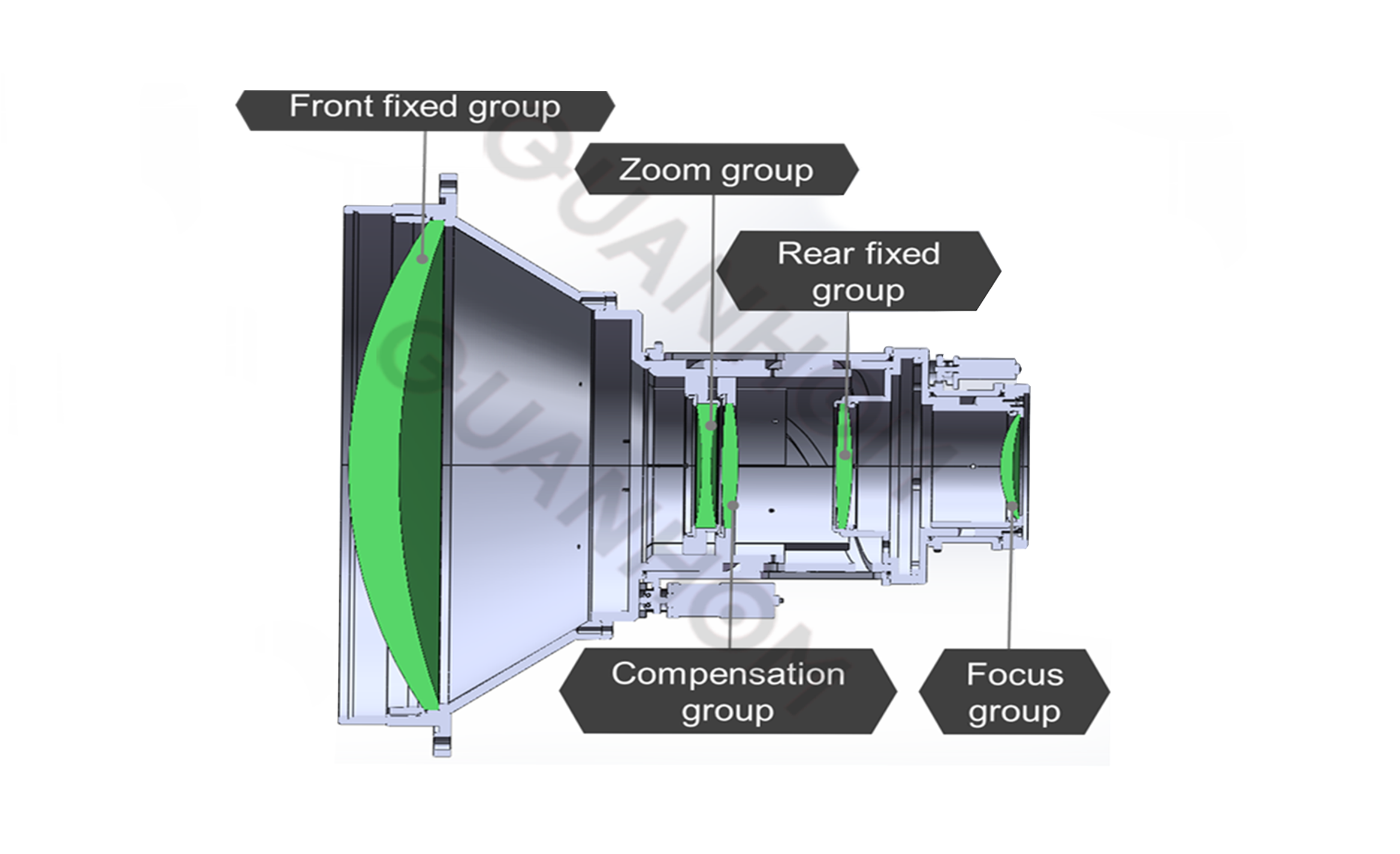
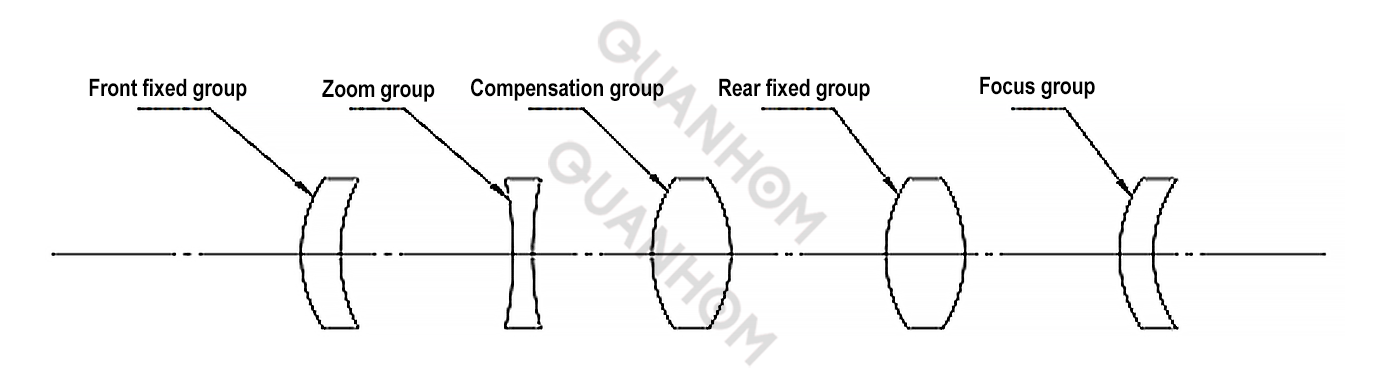
Therefore, in a zoom optical system, the focal length of multiple lens groups and the distance between them jointly determine the focal length of the system. As shown in the figure below, in general, a zoom optical system consists of five components: a front fixed lens group, a zoom lens group, a compensation lens group, a rear fixed lens group, and a focus group. Therefore, the focal lengths of the multiple elements in a zoom optical system and the distance between each element together determine the focal length of the system. When adjusting focal length, the zoom lens group and the compensation lens group move in the corresponding direction according to the optical design parameters, in order to change the distance between the lenses to achieve a change in focal length.
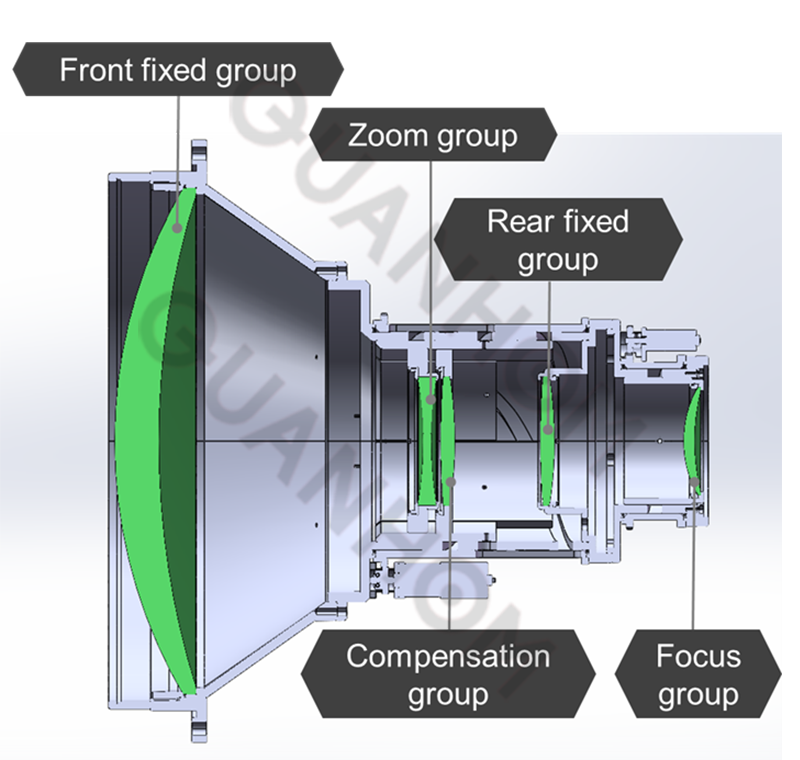
Take the GCZ103013D as an example: its F number is 0.85-1.3, the focal length is 30-300mm. This is an optical transmission system comprising five lens groups: a front fixed group, a zoom group, a compensation group, a rear fixed group, a focus group. The zoom group performs linear movement, while the compensation group undergoes a relatively small, nonlinear movement to maintain clear imaging throughout the zoom process. The focus group performs linear movement to adjust focus in response to defocus caused by temperature changes.
(I)Calculation of cam curve for the system
After the optical structure parameters (radius, spacing, material) of each lens group are determined, it is also necessary to calculate the displacement of the zoom group and the compensation group, so as to process the cam track.
According to Gaussian optics, let the moving distance of the zoom group be x. To ensure that the image plane keep stable, the displacement y of the compensation group can be calculated by:
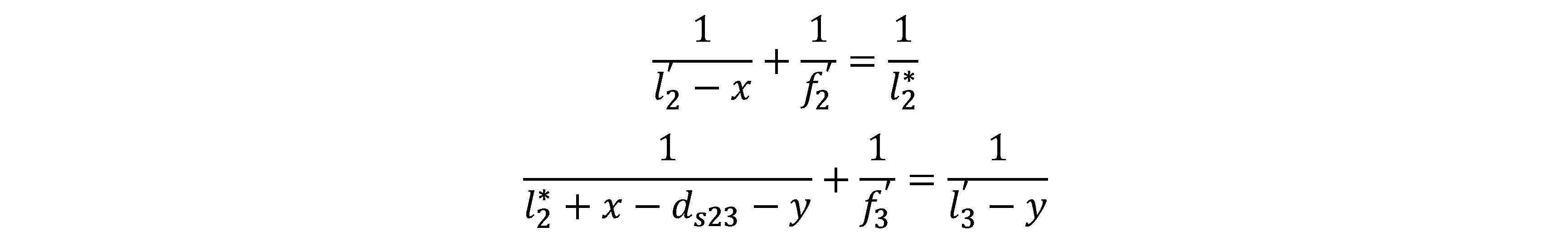
In the formula: ds23 is the interval between the zoom group and the compensation group at short focal length; f2' is the focal length of the zoom group; f3' is the focal length of the compensation group; l2' is the image distance of the zoom group; l3' is the image distance of the compensation group. Eliminate the zoom group object distance l2* in the above two formulas. The simplified formula is as follows:
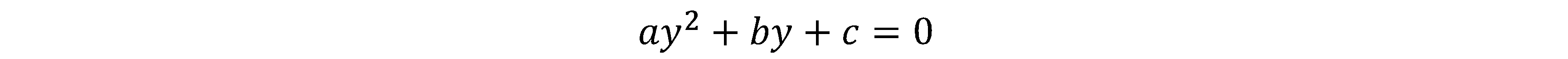
In the formula:
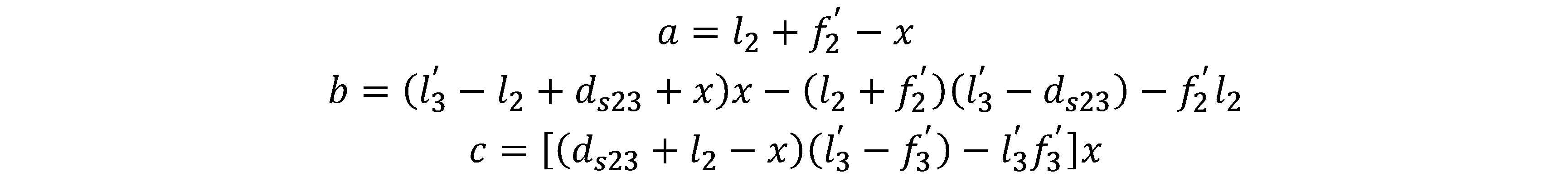
Solution:
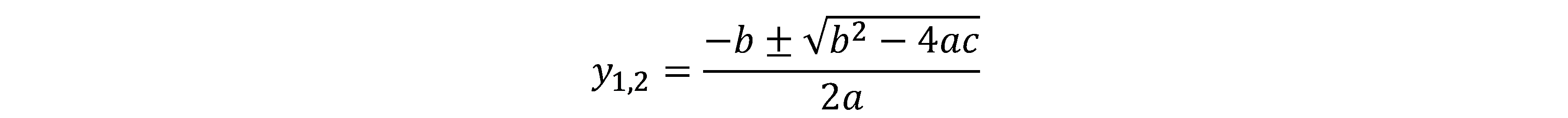
The compensation displacement y takes the root with the smaller absolute value. If there is no real root of y during zoom group movement, it indicates a break in the curve, making continuous zooming impossible. Then the optical system needs to be recalculated, adjusted, optimized, etc.
Based on the above solution formula, the cam curve of the zoom system is shown in the figure. It can be seen that the maximum stroke of the zoom group is 54mm, and the maximum stroke of the compensation group is 27.5mm; the curve of the compensation group changes smoothly, and the two groups of curves can be used for cam track processing.
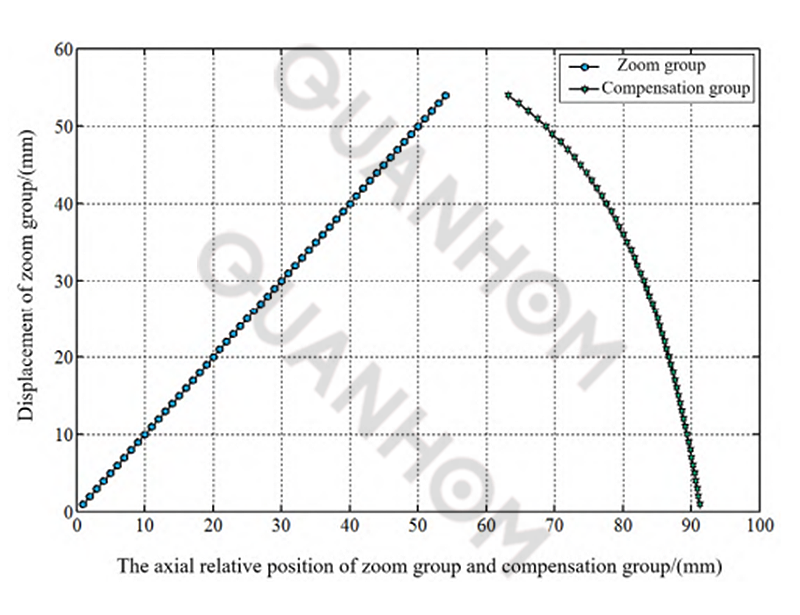
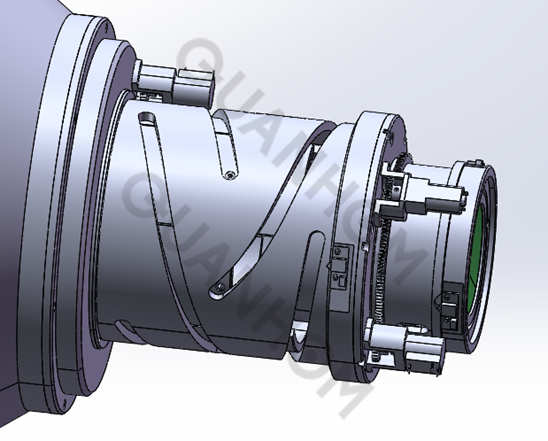
(II) Design of zoom mechanism
The zoom cam rotates without gaps under the action of the ball and cam retainer ring, effectively reducing the output torque of the motor by converting sliding friction into rolling friction. When the motor drives the cam to rotate, the cam transmits the motion to the zoom slide and the compensation slide through the guide pin. Under the guidance of straight grooves on the main lens tube, the zoom slide and compensation slide convert the cam's rotational motion into the slide's parallel movement along the optical axis direction, thereby achieving zooming. The zoom curve groove and the compensation curve groove on the cam are precisely processed to ensure that the zoom and compensation movements are corresponding to each other point by point, maintaining clear throughout continuous zooming.
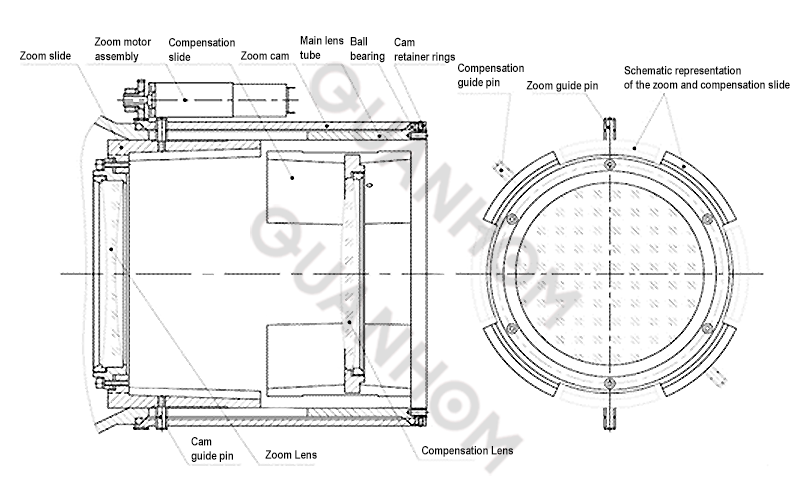
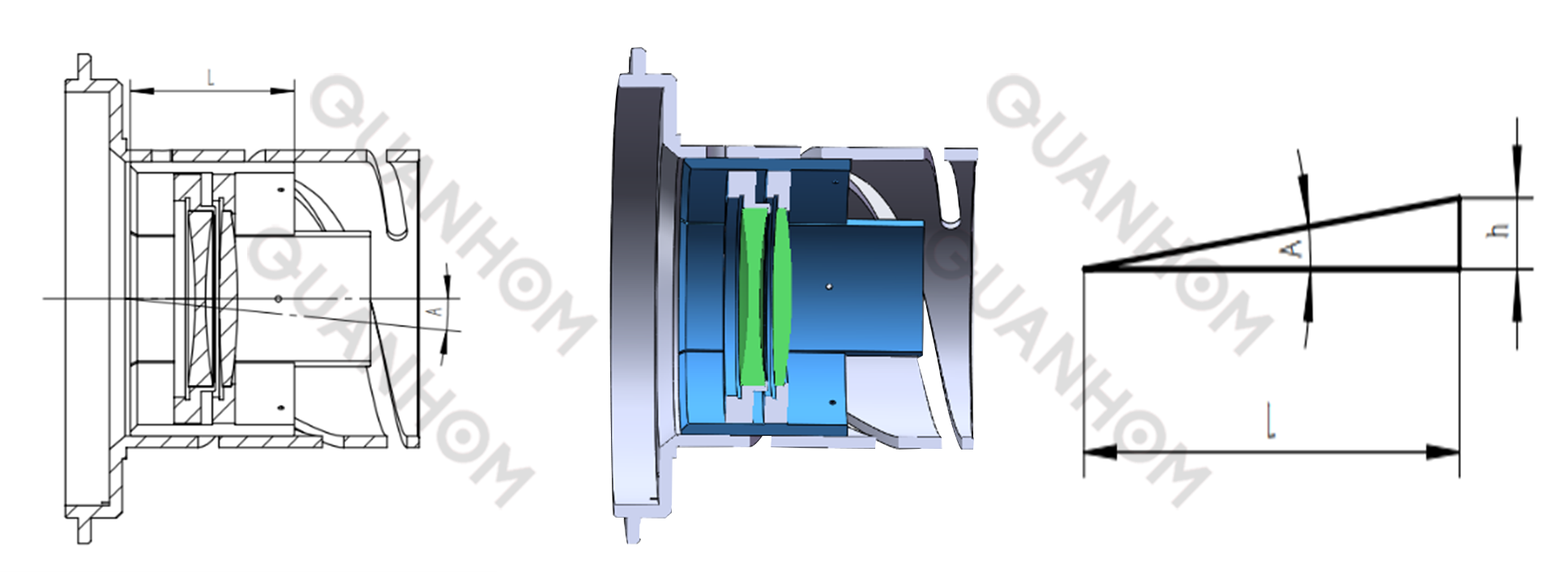
Since the system requires the optical axis consistency to be less than A during the zooming process, the effective length matching of the zoom slide, compensation slide and main lens tube is L mm, and the gap between the slide and the tube should be less than h=L×tan(A). Therefore, the zoom slide and compensation slide are required to match with the main lens tube, and the gap is controlled within the range of h to ensure smooth movement of the zoom slide and compensation slide while meeting the requirements of optical axis stability.
(III) Finite element analysis of cam
According to the requirements of environmental adaptability, the lens needs to withstand a maximum impact force of 10g, ensuring the deformation of the slide and cam remains within the optically allowable error range to meet the performance requirements. The zoom slide, compensation slide, and cam are made from 7A09 superhard aluminium, with a Poisson's ratio of 0.33, an elastic modulus of 73GPa, a yield strength of ≥400MPa, and a density of 2.78×10-6kg/mm3. The zoom assembly weighs 0.4kg, the compensation assembly weighs 0.4kg, and the cam weighs 0.5kg.
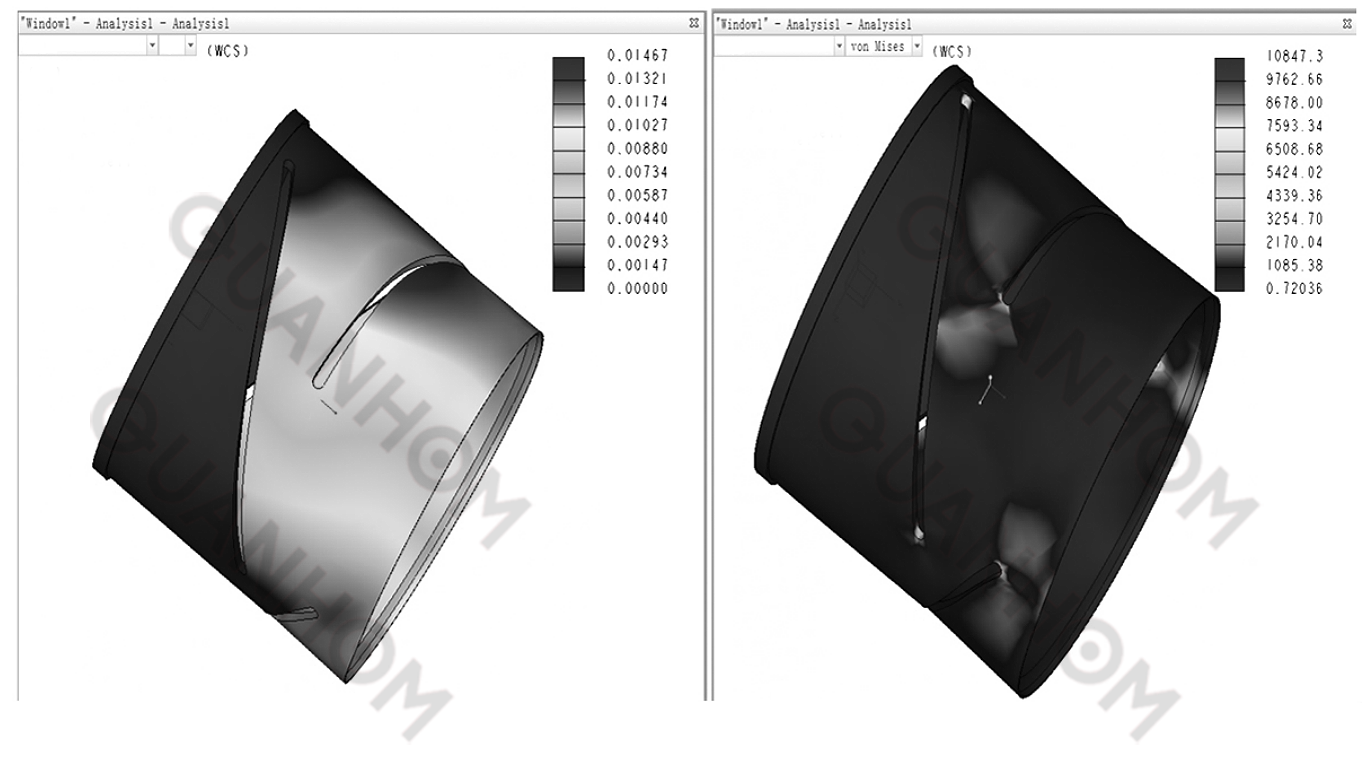
Given the structural characteristics, the cam experiences the maximum axial force through the guide pins during shocks. For axial force of the cam, each cam curve groove experiences an axial force of 10×0.4/2kg=20N, and the cam axial support end experiences a reaction force of 10×(0.4+0.4+0.5)kg=130N. A fixed displacement is applied at the cam support end for static analysis. The analysis results are shown in the figure below. The maximum deformation is 0.01467mm, which is within the optical allowable deformation range. The maximum stress is 10.85MPa<yield strength 400MPa, so the cam strength meets the requirements.
(IV) Finite element analysis of the slide
(IV) Finite element analysis of the slide
Due to the structural characteristics, the zoom slide and the compensation slide experience maximum deformation under radial forces, with a maximum force of 10×0.4kg=40N. A fixed displacement is applied to the inner diameter of the slide for static analysis. The analysis results are shown in the figure below. The maximum deformation of the zoom slide is 0.00683mm, the maximum stress is 3.2MPa, while the maximum deformation of the compensation slide is 0.00135mm, and the maximum stress is 1.47MPa. The deformation is brought into the optical software for simulation, and there is almost no effect on the imaging. Therefore, the strength of the zoom slide and the compensation slide meets the requirements.
(V) Strength verification of zoom guide pin
Each zoom and compensation assembly weighs 0.4kg, and the maximum impact force is 40N under 10g shock. Each guide pin experiences a maximum shear force of 20N. The minimum cross-sectional area of the guide pin is 4.52×10-4m2 and made from HPb59-1 brass, and the allowable shear stress is 200MPa.
The maximum shear stress on the guide pin is: T = 20/(4.52 × 10-4), Pa = 4.42 ×104Pa <200MPa, so the pin strength meets the requirements.
